|
Concours
Capes
: Etude
électrique du rotor du moteur
asynchrone
2007
|
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
Les vecteurs sont
écrits en gras et en
bleu.
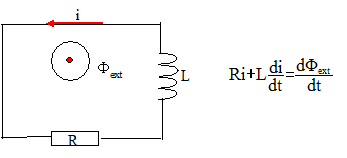
Equation différentielle qui régit le courant i(t) dans la bobine du rotor :
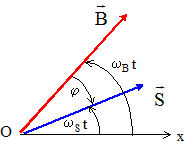
Expression de Fext en fonction de t, B0, S, wB, wS et j. Fext(t) = B(t) . S(t) avec Bx(t) = -B0sin( wB t ) ; By(t) =B0 cos( wB t ) et Sx(t) = S sin( wS t -j) ; Sy(t) =B0 cos( wS t -j ) Fext(t) = Bx(t)Sx(t) + By(t)Sy(t) Fext(t) =B0S [-sin( wB t )sin( wS t -j) +cos( wB t )cos( wS t -j )] Or -sin( wB t )sin( wS t -j) +cos( wB t )cos( wS t -j ) = cos (( wB-wS)t +j) Fext(t) =B0Scos (( wB-wS)t +j).
Expression de Imax en fonction de w, R, L, B0 et S : L''équation différentielle est résolue par la méthode des nombres complexes ; on pose w = wB-wS Ri + Ldi/dt =d Fext/dt ; Fex = B0Scos( wt +j) ; i(t) = Imax cos(wt+j-Y).
R I max exp j(j-Y) + jLwImaxexp j(j-Y)= jw B0Sexp jj. (R+jLw)I maxexp j(-Y) = jw B0S Par suite en égalant les modules [R2+(Lw)2 ] I2 max = (w B0S)2. Imax= w B0S [R2+(Lw)2 ] -½. arg [(R+jLw)I max] -Y = arg ( jw B0S) Y = arg ( jw B0S) - arg [(R+jLw)I max] arg ( jw B0S) = ½p ; arg [(R+jLw)I max] = tan-1(Lw/R). Y =½p -arctan(Lw/R). ½p -Y =arctan(Lw/R) ou sin(½p -Y )= cosY =Lw /[R2+(Lw)2 ] -½ .
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|